Heart rocker: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trailing_wheel "Trailing wheel", <i>Wikipedia</i>] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trailing_wheel "Trailing wheel", <i>Wikipedia</i>] | ||
* [https://www.chaski.org/homemachinist/viewtopic.php?f=45&t=98991&start=12 "A Real Dirty Job", <i>Chaski.org</i>, page 2] | * [https://www.chaski.org/homemachinist/viewtopic.php?f=45&t=98991&start=12 "A Real Dirty Job", <i>Chaski.org</i>, page 2] | ||
* [http://cs.trains.com/mrr/f/13/p/190994/2085347.aspx "Loco lead/trail wheel support mechanism", <i>Trains.com</i>] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:35, 1 November 2018
Alfred W. Bruce wrote in The Steam Locomotive in America:
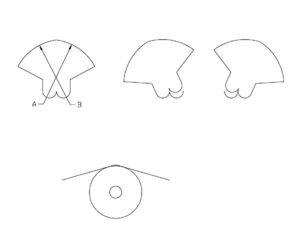
- The inverted-rocker device was introduced about 1914. The inverted rocker was a heart-shaped rocker resting on two rolling contacts at the bottom and supporting two inclined planes at the top--one on each side of its apex center point. Thus movement in either direction produces a rolling-contact support which permits ample lateral movement with nearly any desired resistance characteristic, a quality that has retained this device in use today [approx. 1952].
Gallery
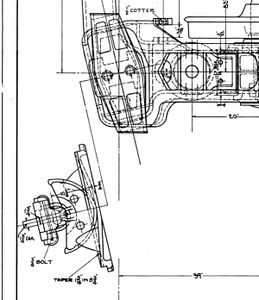
Attached is a portion of the trailer truck arrangement drawing for a UP Big Boy. You can see the way the prototype rocker, rocker seat and bearing, and the rocker plate (which is mounted on the bottom of the frame cradle) were designed. Notice the "teeth" (or "toes") at the bottom of the rocker plate.